Understanding the Weight of an Empty Tractor-Trailer
Knowing the weight of your empty tractor-trailer is crucial for safety, legal compliance, and efficient operations. This seemingly simple question has a complex answer, as the weight varies significantly depending on several factors. Ignoring this can lead to hefty fines, increased fuel consumption, and safety hazards. Let's delve into the details. For more on trailer dimensions, check out this helpful resource.
Factors Influencing Empty Weight
Several interconnected factors determine the weight of your empty rig. These include:
- Tractor Unit: The weight of the tractor itself—engine, cab, chassis—varies widely based on make, model, and added features. Expect a range from 10,000 to 25,000 pounds.
- Trailer Type: Different trailers have vastly different weights. A standard dry van typically weighs 10,000–15,000 pounds empty, while a lowboy trailer designed for heavy equipment can weigh significantly more (15,000–25,000 pounds). Refrigerated trailers (reefers) also add substantial weight due to their refrigeration units (12,000–18,000 pounds).
- Additional Equipment: Auxiliary power units (APUs), fuel tanks, toolboxes, and other added components all contribute to the overall weight. These can easily total several thousand pounds.
"The weight of your tractor and trailer is not just a number, but a critical factor in your safety and legal compliance," states John Miller, Safety Director at National Trucking Association.
Average Weight: A General Estimate
While a precise number is impossible without knowing the specifics of your rig, a reasonable estimate for the combined weight of an empty tractor and trailer is around 30,000 pounds. However, this is just a ballpark figure; the actual weight could be considerably higher or lower.
Did you know? A seemingly small addition, like a larger fuel tank, can add hundreds of pounds to your rig's weight.
Why Knowing the Weight Matters: Safety and Legal Compliance
Understanding your rig's weight isn't merely for curiosity; it's essential for:
- Safety: Overloading your truck increases fuel consumption, accelerates wear and tear on components (tires, brakes), and drastically increases the risk of accidents. Proper weight distribution is also critical for safe handling.
- Legal Compliance: Exceeding weight limits (gross vehicle weight rating or GVWR, or axle weight limits) leads to significant fines and potential legal repercussions. These limits vary by state and type of vehicle.
"Inaccurate weight calculations can lead to serious consequences," warns Sarah Chen, a transportation lawyer based in Atlanta. "Regular weigh-ins and careful monitoring are crucial for compliance and safety."
Calculating and Managing Your Tractor-Trailer's Weight
Accurate weight management is paramount. This section outlines the steps to determine your rig's weight and stay within legal limits.
Determining Your Rig's Empty Weight (Curb Weight)
- Consult Manufacturer Specifications: Begin with the information provided by the manufacturer of your tractor and trailer. This will give you a starting point, but keep in mind that this may not account for additional equipment.
- Weigh Your Rig: Use a certified truck scale for the most accurate measurement. Obtain a weight breakdown by axle, as axle weight limits are also strictly regulated.
- Document Your Findings: Keep detailed records of your weigh-ins. This is crucial for audits and demonstrating compliance.
Important Fact: Axle weight limits are often more restrictive than the overall GVWR. Exceeding axle weight limits leads to citations even if the total GVWR is within legal parameters.
Calculating Gross Vehicle Weight (GVWR) and Payload
Once you know your empty weight, calculating your permissible payload is straightforward:
GVWR = Empty Weight + Cargo Weight
In most US states, the maximum legal GVWR for tractor-trailers is 80,000 pounds. However, always check your state's specific regulations, as these can vary. Subtracting your empty weight from the legal GVWR provides your maximum payload capacity.
Rhetorical Question: Why is it essential to accurately calculate your payload capacity before loading your cargo?
Axle Weight Limits and Distribution
Understanding axle weight limits is equally critical. Improper weight distribution can lead to violations, even if your overall GVWR is within legal limits. Typical axle weight limits:
| Axle Type | Weight Limit (lbs) (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Steer Axle | 12,000 |
| Drive Tandem | 34,000 |
| Trailer Tandem | 34,000 |
Note: These are approximate values; always check your state's specific regulations for precise limits.
Weight Redistribution Techniques
If you find yourself overweight on any axle, you can try several techniques to redistribute weight:
- Repositioning Cargo: Shifting heavier items toward the center of gravity often resolves axle weight issues.
- Fifth Wheel Adjustment: Minor adjustments to the fifth wheel position can influence weight distribution.
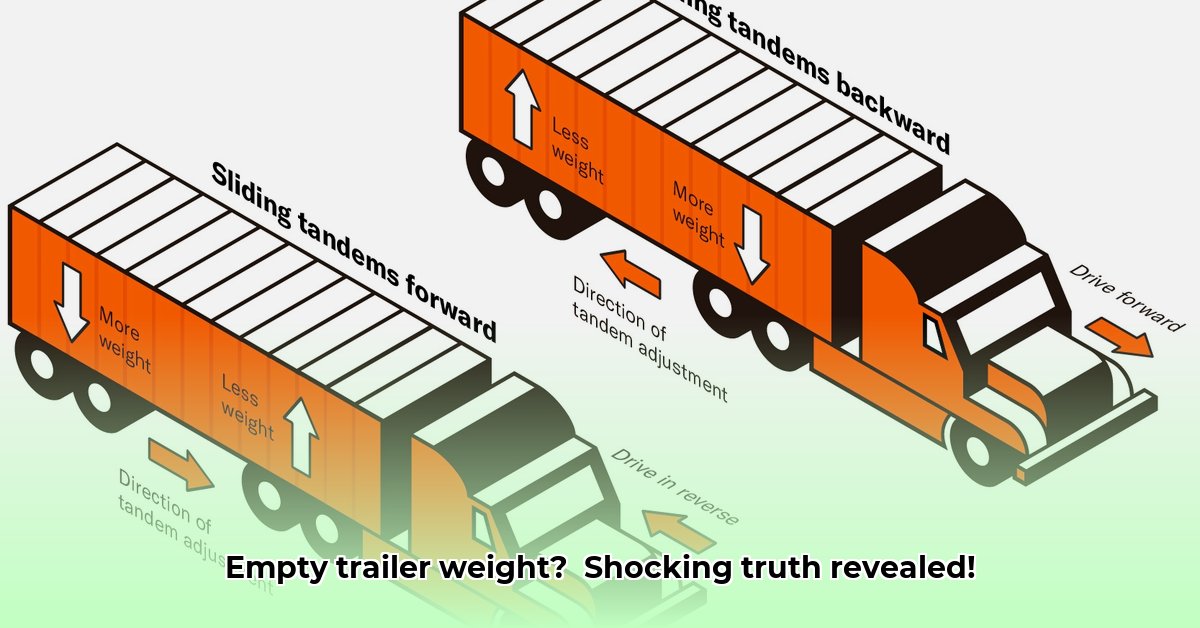
- Tandem Axle Shifting: If your trailer has sliding tandem axles, adjusting their position can help balance the weight.
Always prioritize safety and legal compliance. Consult a qualified professional if you're unsure about weight redistribution techniques.
The Importance of Regular Weigh-Ins
Regular weigh-ins are paramount for maintaining compliance and safety. They allow you to monitor your weight, identify potential issues early, and avoid costly fines and accidents.
Conclusion: Prioritize Accurate Weight Management
Accurately determining and managing the weight of your empty tractor-trailer is not just a matter of compliance; it is a critical element of responsible and safe operation. By following these steps and staying informed about regulations, you can minimize risks, optimize your operation, and maximize your profitability.